Why Monitoring Premature Ventricular Contractions is More Important for Firefighters

Premature ventricular contractions (PVC) are extra beats that can disrupt the normal pumping rhythm of the heart. PVC’s can be associated with increased levels of adrenaline in the body that may be caused by:
- Caffeine
- Tobacco
- Exercise
- Anxiety
- Possibly injury to the heart muscle from coronary artery disease
- Congenital heart disease
- High blood pressure.
PVC’s can affect the heart in different ways. At the moment they occur they decrease cardiac output by not allowing the heart to pump out the normal amount of blood. If left untreated and if they occur often, they can decrease the heart muscle's ability to forcefully pump out blood at higher intensities. They can increase the risk of developing dangerous heart rhythms and should be monitored through stress testing which may warrant further investigation and studies. PVCs are often considered benign in normal healthy individuals but since the rigors of firefighting can place them in scenarios where the intensities of work can be high, extra caution should be taken when exercise induced PVC’s are recorded.
The image below illustrates the effects of PVC’s.
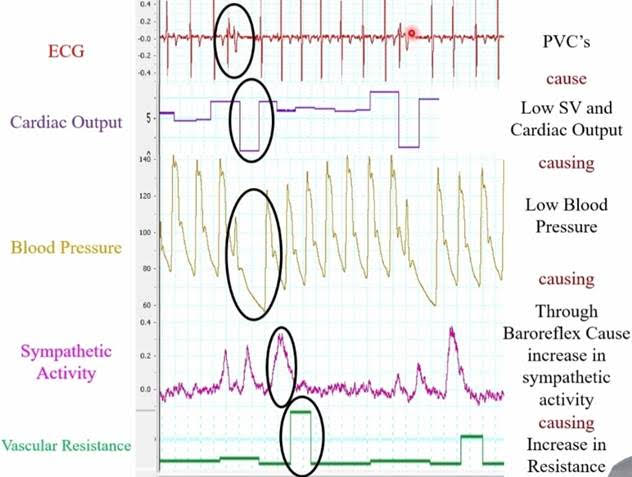
In the image, you can see how 1 PVC can affect multiple processes in the body.
Ventricular electrical conduction is usually a symptom of something greater in the older patient population - cardiovascular disease.
Written by Alex Jesko, Exercise Physiologist